A hundred years ago, the formidable guide, scholar and cultural authority Mākereti Papakura was documenting village life, politics and high-society visits in Whakarewarewa. Now, her whanaunga June Northcroft-Grant revisits those diary pages with fresh eyes.
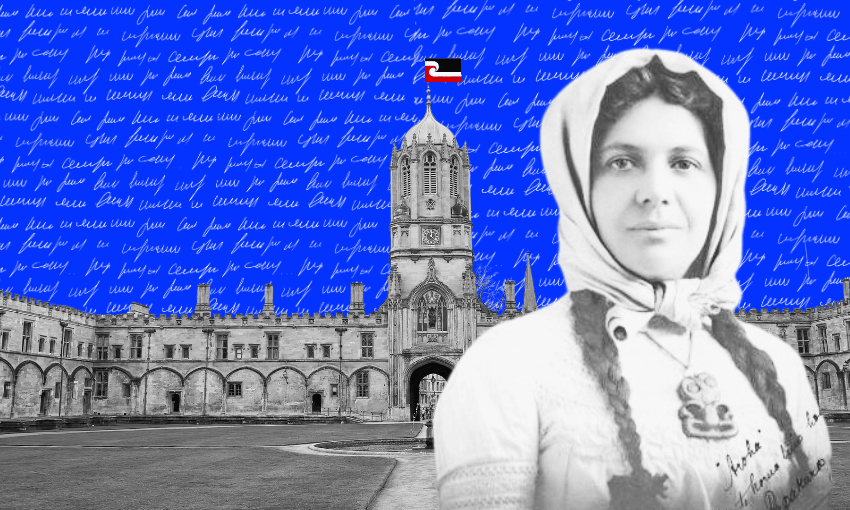
This year, more than a century after she enrolled at Oxford University, pioneering Te Arawa scholar Mākereti Papakura will be awarded a posthumous Master of Philosophy in Anthropology from the University of Oxford. The recognition honours her extraordinary contribution to ethnography – one that challenged colonial norms by documenting the richness of Māori life from within.
Born in Matatā in 1873 and raised in Whakarewarewa, Mākereti was a cultural authority, a beloved guide and the first known indigenous woman to enrol at Oxford. Her thesis, published after her sudden death in 1930 as The Old-Time Māori, remains a landmark work. For her descendants and the people of Tūhourangi – Ngāti Wāhiao, the honour is a long-overdue affirmation of a life lived boldly across worlds. And for one of her whānau, reading through her 1907 diary reveals just how alive, political and purposeful that life really was.
As a child, I was captivated by a black-and-white photo in my parents’ old album. It showed an enigmatic Māori woman wearing a headscarf and a large hei tiki, staring out with knowing eyes. My father Henry, who was raised in Whakarewarewa from 1915 by his kuia Rakera, told me she was his mother’s cousin: Mākereti Papakura. He called her Whaea. She had lived in England, spoke “like the Queen,” and once returned to the village in the 1920s for a brief visit. To my father, she was a glamorous figure – worldly and impressive.
I was in my forties when I rediscovered her story. I remembered that Mākereti had left a diary behind in her sister Bella’s home, Teawaimanukau. Reading it as an adult was something else entirely. The names she wrote of – Apirana, Maui, Te Rangihiroa, Tawa – were no longer just names. I knew who they were, what they meant to us, and to Aotearoa. Her diary, written in 1907, reveals a vibrant life at Whakarewarewa: hosting visitors from across the world, guiding tourists through geothermal wonders, and sharing meals and conversations with some of the most influential Māori thinkers of her generation.
Sir Apirana Ngata, Sir Maui Pomare, and Sir Peter Buck (Te Rangihiroa) feature regularly, not as distant historical figures, but as friends. Alongside them, captain Gilbert Mair (Tawa), a close family friend, appears frequently in her entries. Together, these young leaders formed what became known as the Young Māori Party – a visionary collective working to uplift Māori health, education, land development and cultural pride.
Friday February 8, 1907: Tawa only in Ohinemutu – arranging Porimi’s funeral. Spent evening & had dinner with us… Brought some lovely peaches. He is a dear old father to us. Letter in Herald by W.B. Te Kuiti. A beautiful article written by an educated man and one who understands the Māori race. Kia ora W.B. Te Kuiti A Ake! Ake! Ake!
One entry records Te Rangihiroa and his wife coming to live in the village. Others note her deep affection for her sister Bella, her grief when sending young nieces to boarding school, and the small joys and outrages of daily life. From lighthearted mentions of local observers satirising her haka, to fury at a policeman trying to stop villagers from bathing in their own pools, her voice is vivid.
Sunday June 30, 1907: Constable came out and said Māoris were not to bathe in roadside bath and he took down the names of the people there. Like their impudence to talk and interfere with things on our own private grounds.
The diary also captures moments of national significance. During Ngata’s campaign for parliament, Mākereti records the excitement, the vehicles used to shuttle voters, the gatherings and the performances.
Wednesday December 4, 1907: Great excitement over our own election for Apirana Ngata. We had a motorcar to convoy our people backwards and forwards… Big lunch at Wahiao for all the tribes and our own people. Everything a huge success.”
And then, this mysterious note:
Tuesday November 19, 1907: A day never to be forgotten.
No explanation follows. But in the back of the diary is a name and address: Richard Staples-Brown, Brampton, Oxfordshire. Four years later, Mākereti would marry him. They later divorced. And she, ever determined, went on to enrol at Oxford University to study anthropology.
She was in her fifties, living modestly, struggling with illness, and racing to finish her thesis when she died suddenly in 1930. Her friend and fellow anthropologist, Thomas K. Penniman, kept his promise to her. He helped ensure her manuscript, The Old-Time Maori, was published posthumously. In a 1936 letter to Bella Wiari, he wrote:
“Those of us who loved her and admired the Māori people are anxious that her work should be published without any mistakes, so that both the younger people of Te Arawa and the people of the world should know how fine the old Māori civilisation was, and what it has to contribute to the world.”
That sentiment still rings true. Reading her diary over a century later, I see not only the voice of a pioneering scholar and cultural guide but the enduring wairua of a woman who loved her people, her village, and her world.